In this Azure Interview Questions Blog, following are the sections we have covered:
Apart from this Azure Interview Questions Blog, if you want to get trained from professionals on this technology, you can opt for a structured training from edureka! Click below to know more.
Apart from this Azure Interview Questions Blog, if you want to get trained from professionals on this technology, you can opt for a structured training from edureka! Click below to know more.
12. Are data disks supported within scale sets?
Explanation: Yes. A scale set can define an attached data disk configuration that applies to all VMs in the set. Other options for storing data include:
- Azure files (SMB shared drives)
- OS drive
- Temp drive (local, not backed by Azure Storage)
- Azure data service (for example, Azure tables, Azure blobs)
- External data service (for example, remote database)
13. What is an Availability Set?
Explanation: An availability set is a logical grouping of VMs that allows Azure to understand how your application is built to provide redundancy and availability. It is recommended that two or more VMs are created within an availability set to provide for a highly available application and to meet the 99.95% Azure SLA. When a single VM is used with Azure Premium Storage, the Azure SLA applies for unplanned maintenance events.
Apart from this Azure Interview Questions Blog, if you want to get trained from professionals on this technology, you can opt for a structured training from edureka! Click below to know more.
14. What are Fault Domains?
Explanation: A fault domain is a logical group of underlying hardware that share a common power source and network switch, similar to a rack within an on-premise data-centers. As you create VMs within an availability set, the Azure platform automatically distributes your VMs across these fault domains. This approach limits the impact of potential physical hardware failures, network outages, or power interruptions.
15. What are Update Domains?
Explanation: An update domain is a logical group of underlying hardware that can undergo maintenance or can be rebooted at the same time. As you create VMs within an availability set, the Azure platform automatically distributes your VMs across these update domains. This approach ensures that at least one instance of your application always remains running as the Azure platform undergoes periodic maintenance. The order of update domains being rebooted may not proceed sequentially during planned maintenance, but only one update domain is rebooted at a time.
16. What are Network Security Groups?
Explanation: A network security group (NSG) contains a list of Access Control List (ACL) rules that allow or deny network traffic to subnets, NICs, or both. NSGs can be associated with either subnets or individual NICs connected to a subnet. When an NSG is associated with a subnet, the ACL rules apply to all the VMs in that subnet. In addition, traffic to an individual NIC can be restricted by associating an NSG directly to a NIC.
17. Do scale sets work with Azure availability sets?
Explanation: Yes. A scale set is an implicit availability set with 5 fault domains and 5 update domains. Scale sets of more than 100 VMs span multiple placement groups, which are equivalent to multiple availability sets. An availability set of VMs can exist in the same virtual network as a scale set of VMs. A common configuration is to put control node VMs (which often require unique configuration) in an availability set and put data nodes in the scale set.
18. What is a break-fix issue?
Explanation: Technical problems are called break-fix issue, it is an industry term which refers to “work involved in supporting a technology when it fails in the normal course of its function, which requires intervention by a support organization to be restored to working order”.
19. Why is Azure Active Directory used?
Explanation: Azure Active Directory is an Identity and Access Management system. It is used to grant access to your employees to specific products and services in your network. For example: Salesforce.com, twitter etc. Azure AD has some in-built support for applications in its gallery which can be added directly.
20. What happens when you exhaust the maximum failed attempts for authenticating yourself via Azure AD?
Explanation: We use a more sophisticated strategy to lock accounts. This is based on the IP address of the request and the passwords entered. The duration of the lockout also increases based on the likelihood that it is an attack.
21. Where can I find a list of applications that are pre-integrated with Azure AD and their capabilities?
Explanation: Azure AD has around 2600 pre-integrated applications. All pre-integrated applications support single sign-on (SSO). SSO let you use your organizational credentials to access your apps. Some of the applications also support automated provisioning and de-provisioning.
Apart from this Azure Interview Questions Blog, if you want to get trained from professionals on this technology, you can opt for a structured training from edureka! Click below to know more.
22. How can I use applications with Azure AD that I’m using on-premises?
Explanation: Azure AD gives you an easy and secure way to connect to the web applications you choose. You can access these applications in the same way you access your SaaS apps in Azure AD, no need for a VPN to change your network infrastructure.
23. What is Azure Service Fabric?
Explanation: Azure Service Fabric is a distributed systems platform that makes it easy to package, deploy, and manage scalable and reliable micro-services. Service Fabric also addresses the significant challenges in developing and managing cloud applications. Developers and administrators can avoid complex infrastructure problems and focus on implementing mission-critical, demanding workloads that are scalable, reliable, and manageable. Service Fabric represents the next-generation middleware platform for building and managing these enterprise-class, tier-1, cloud-scale applications.
24. What is a VNet?
Explanation: VNet is a representation of your own network in the cloud. It logically isolates your instances launched in the cloud, from the rest of your resources.
25. What are the differences between Subscription Administrator and Directory Administrator?
Explanation: By default, one is assigned the Subscription Administrator role when he/she signs up for Azure. A subscription admin can use either a Microsoft account or a work or school account from the directory that the Azure subscription is associated with. This role is authorized to manage services in the Azure portal. If others need to sign in and access services by using the same subscription, you can add them as co-admins.
Azure AD has a different set of admin roles to manage the directory and identity-related features. These admins will have access to various features in the Azure portal or the Azure classic portal. The admin’s role determines what they can do, like create or edit users, assign administrative roles to others, reset user passwords, manage user licenses, or manage domains.
26. Are there any scale limitations for customers using managed disks?
Explanation: Managed Disks eliminates the limits associated with storage accounts. However, the number of managed disks per subscription is limited to 2000 by default.
27. What is the difference between Service Bus Queues and Storage Queues?
Explanation: The Azure Storage Queue is simple and the developer experience is quite good. It uses the local Azure Storage Emulator and debugging is made quite easy. The tooling for Azure Storage Queues allows you to easily peek at the top 32 messages and if the messages are in XML or Json, you’re able to visualize their contents directly from Visual Studio Furthermore, these queues can be purged of their contents, which is especially useful during development and QA efforts.
The Azure Service Bus Queues are evolved and surrounded by many useful mechanisms that make it enterprise-worthy! They are built into the Service Bus and are able to forward messages to other Queues and Topics. They have a built-in dead-letter queue and messages have a time to live that you control, hence messages don’t automatically disappear after 7 days.
Furthermore, Azure Service Bus Queues have the ability of deleting themselves after a configurable amount of idle time. This feature is very practical when you create Queues for each user, because if a user hasn’t interacted with a Queue for the past month, it automatically gets clean it up. Its also a great way to drive costs down. You shouldn’t have to pay for storage that you don’t need. These Queues are limited to a maximum of 80gb. Once you’ve reached this limit your application will start receiving exceptions.
28. What is Azure Redis Cache?
Redis is an open source (BSD licensed), in-memory data structure store, used as a database, cache and message broker. Azure Redis Cache is based on the popular open-source Redis cache. It gives you access to a secure, dedicated Redis cache, managed by Microsoft, and accessible from any application within Azure. It supports data structures such as strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets with range queries, bitmaps, hyperloglogs and geospatial indexes with radius queries.
Apart from this Azure Interview Questions Blog, if you want to get trained from professionals on this technology, you can opt for a structured training from edureka! Click below to know more.
29. Why doesn’t Azure Redis Cache have an MSDN class library reference like some of the other Azure services?
Explanation: Microsoft Azure Redis Cache is based on the popular open source Redis Cache and can be accessed by a wide variety of Redis clients for many programming languages. Each client has its own API that makes calls to the Redis cache instance using Redis commands.
Because each client is different, there is not one centralized class reference on MSDN, and each client maintains its own reference documentation. In addition to the reference documentation, there are several tutorials showing how to get started with Azure Redis Cache using different languages and cache clients. To access these tutorials, see How to use Azure Redis Cache and click the desired language from the language switcher at the top of the article.
30. What are Redis databases?
Explanation: Redis Databases are just a logical separation of data within the same Redis instance. The cache memory is shared between all the databases and actual memory consumption of a given database depends on the keys/values stored in that database. For example, a C6 cache has 53 GB of memory. You can choose to put all 53 GB into one database or you can split it up between multiple databases.
31. Is it possible to add an existing VM to an availability set?
Explanation: No. If you want your VM to be part of an availability set, you need to create the VM within the set. There currently no way to add a VM to an availability set after it has been created.
32. What are the username requirements when creating a VM?
Explanation: Usernames can be a maximum of 20 characters in length and cannot end in a period (“.”).
The following usernames are not allowed:
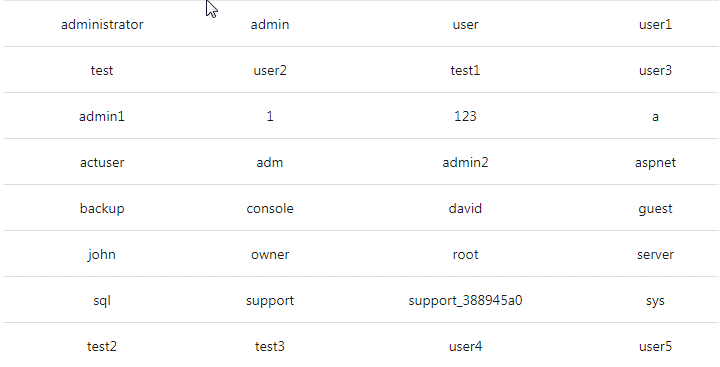
33. What are the password requirements when creating a VM?
Explanation: Passwords must be 12 – 123 characters in length and meet 3 out of the following 4 complexity requirements:
- Have lower characters
- Have upper characters
- Have a digit
- Have a special character (Regex match [W_])
The following passwords are not allowed:
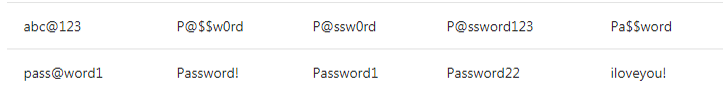
Apart from this Azure Interview Questions Blog, if you want to get trained from professionals on this technology, you can opt for a structured training from edureka! Click below to know more.
Related Article: Difference Between AWS vs Azure!
34. How much storage can I use with a virtual machine?
Explanation: Each data disk can be up to 1 TB. The number of data disks which you can use depends on the size of the virtual machine.
Azure Managed Disks are the new and recommended disk storage offerings for use with Azure Virtual Machines for persistent storage of data. You can use multiple Managed Disks with each Virtual Machine. Managed Disks offer two types of durable storage options: Premium and Standard Managed Disks.
Azure storage accounts can also provide storage for the operating system disk and any data disks. Each disk is a .vhd file stored as a page blob. You can learn more about this from the MS Azure certification.
35. How can one create a Virtual Machine in Powershell?
# Define a credential object
$cred = Get-Credential
# Create a virtual machine configuration
$vmConfig = New-AzureRmVMConfig -VMName myVM -VMSize Standard_DS2 |
` Set-AzureRmVMOperatingSystem -Windows -ComputerName myVM -Credential $cred |
` Set-AzureRmVMSourceImage -PublisherName MicrosoftWindowsServer -Offer WindowsServer `
-Skus 2016-Datacenter -Version latest | Add-AzureRmVMNetworkInterface -Id $nic.Id
36. How to create a Network Security Group and a Network Security Group Rule?
# Create an inbound network security group rule for port 3389
$nsgRuleRDP = New-AzureRmNetworkSecurityRuleConfig -Name myNetworkSecurityGroupRuleRDP -Protocol Tcp `
-Direction Inbound -Priority 1000 -SourceAddressPrefix * -SourcePortRange * -DestinationAddressPrefix * `
-DestinationPortRange 3389 -Access Allow
# Create an inbound network security group rule for port 80
$nsgRuleWeb = New-AzureRmNetworkSecurityRuleConfig -Name myNetworkSecurityGroupRuleWWW -Protocol Tcp `
-Direction Inbound -Priority 1001 -SourceAddressPrefix * -SourcePortRange * -DestinationAddressPrefix * `
-DestinationPortRange 80 -Access Allow
# Create a network security group
$nsg = New-AzureRmNetworkSecurityGroup -ResourceGroupName myResourceGroup -Location EastUS `
-Name myNetworkSecurityGroup -SecurityRules $nsgRuleRDP,$nsgRuleWeb
37. How to create a new storage account and container using Power Shell?
$storageName = "st" + (Get-Random)
New-AzureRmStorageAccount -ResourceGroupName "myResourceGroup" -AccountName $storageName -Location "West US" -SkuName "Standard_LRS" -Kind Storage
$accountKey = (Get-AzureRmStorageAccountKey -ResourceGroupName myResourceGroup -Name $storageName).Value[0]
$context = New-AzureStorageContext -StorageAccountName $storageName -StorageAccountKey $accountKey
New-AzureStorageContainer -Name "templates" -Context $context -Permission Container
38. How can one create a VM in Azure CLI?
az vm create ` --resource-group myResourceGroup ` --name myVM --image win2016datacenter ` --admin-username azureuser ` --admin-password myPassword12
Apart from this Azure Interview Questions Blog, if you want to get trained from professionals on this technology, you can opt for a structured training from edureka! Click below to know more.
39. What are the various power states of a VM?
| Power State | Description |
| Starting | Indicates the virtual machine is being started |
| Running | Indicates that the virtual machine is running |
| Stopping | Indicates that the virtual machine is being stopped |
| Stopped | Indicates that the virtual machine is stopped |
| Deallocating | Indicates that the virtual machine is being deallocated |
| Deallocated | Indicates that the virtual machine is completely removed from the hypervisor but still available in the control plane. Virtual Machines in the deallocated state do not incur compute charges. |
40. How can you retrieve the state of a particular VM?
Get-AzureRmVM `
-ResourceGroupName myResourceGroup `
-Name myVM `
-Status | Select @{n="Status"; e={$_.Statuses[1].Code}}41. How can you stop a VM using Power Shell?
Stop-AzureRmVM -ResourceGroupName myResourceGroupVM -Name "myVM" -Force
42. Why was my client disconnected from the cache?
Explanation: The following are some common reason for a cache disconnect.
- Client-side causes
- The client application was redeployed.
- The client application performed a scaling operation.
- In the case of Cloud Services or Web Apps, this may be due to auto-scaling.
- The networking layer on the client side changed.
- Transient errors occurred in the client or in the network nodes between the client and the server.
- The bandwidth threshold limits were reached.
- CPU bound operations took too long to complete.
- Server-side causes
- On the standard cache offering, the Azure Redis Cache service initiated a fail-over from the primary node to the secondary node.
- Azure was patching the instance where the cache was deployed
- This can be for Redis server updates or general VM maintenance.
43. What is Azure Search?
Explanation: Azure Search is a cloud search-as-a-service solution that delegates server and infrastructure management to Microsoft, leaving you with a ready-to-use service that you can populate with your data and then use to add search to your web or mobile application. Azure Search allows you to easily add a robust search experience to your applications using a simple REST API or .NET SDK without managing search infrastructure or becoming an expert in search.
44. My web app still uses an old Docker container image after I’ve updated the image on Docker Hub. Does Azure support continuous integration/deployment of custom containers?
Explanation: Yes, it does. For private registries, you can update the container by stopping and then re-starting your web app. Alternatively, you can also change or add a dummy application setting to force an update of your container.
Apart from this Azure Interview Questions Blog, if you want to get trained from professionals on this technology, you can opt for a structured training from edureka! Click below to know more.
45. What are the expected values for the Startup File section when I configure the runtime stack?
Explanation: For Node.Js, you specify the PM2 configuration file or your script file. For .NET Core, specify your compiled DLL name. For Ruby, you can specify the Ruby script that you want to initialize your app with.
46. How are Azure Marketplace subscriptions priced?
Explanation:
Pricing will vary based on product types. ISV software charges and Azure infrastructure costs are charged separately through your Azure subscription. Pricing models include:
BYOL Model: Bring-your-own-license. You obtain outside of the Azure Marketplace, the right to access or use the offering and are not charged Azure Marketplace fees for use of the offering in the Azure Marketplace.
Free: Free SKU. Customers are not charged Azure Marketplace fees for use of the offering.
Free Software Trial: Full-featured version of the offer that is promotionally free for a limited period of time. You will not be charged Azure Marketplace fees for use of the offering during a trial period. Upon expiration of the trial period, customers will automatically be charged based on standard rates for use of the offering.
Usage-Based: You are charged or billed based on the extent of your use of the offering. For Virtual Machines Images, you are charged an hourly Azure Marketplace fee. For Data Services, Developer services, and APIs, you are charged per unit of measurement as defined by the offering.
Monthly Fee: You are charged or billed a fixed monthly fee for a subscription to the offering (from the date of subscription start for that particular plan). The monthly fee is not prorated for mid-month cancellations or unused services.
47. What is the difference between “price,” “software price,” and “total price” in the cost structure for Virtual Machine offers in the Azure Marketplace?
Explanation: “Price” refers to the cost of the Azure Virtual Machine to run the software. “Software price” refers to the cost of the publisher software running on an Azure Virtual Machine. “Total price” refers to the combined total cost of the Azure Virtual Machine and the publisher software running on an Azure Virtual Machine.

